Migrate from TFVC to Git
Background
This guide outlines the steps required to migrate your repositories from Microsoft’s TFVC into Git-based repositories.
IMPORTANT : Since TFS 2015 and Azure DevOps both support Git-based repositories, this doesn’t force your teams to move away from them!
Here are the available Git hosting services:
- TFS 2015
- GCcode
- GitHub
In this guide
- Prerequisites
- Create Remote Git Repository
- Clone TFVC to Local Git Repository
- Connect to Remote Git Repository
- Push to Remote Git Repository
- Additional Improvement
- Further Reading
- FAQ
Prerequisites
The prerequisites stay the same regardless of where you choose to host your Git repositories (TFS, GCcode or GitHub).
In order to migrate your TFVC repository into a Git repository you will need:
- Install Git for Windows:
- Navigate to NSD
- From the Application Catalogue, click the Commercial Software tab, then select the GIT link and click Install.
- The installation should take approximately 2 days.
- or download it directly from Git for Windows.
- git-tfs:
- If you don’t have it installed, download it from their GitHub repository. (direct link)
- To install
git-tfs, extract the content of the ZIP file to a folder (i.e.C:\git-tfs) and add that folder’s location to thePATHsystem environment variables.
- Permissions to create repositories in target Git hosting service:
- If you don’t have the appropriate permissions, request them from your team’s source control administrator or request that a new Git repository to be created.
Create Remote Git Repository
First up, you will need to create a new Git repository in your Git hosting service (TFS 2015, GCcode or GitHub).
The process will be different depending on the hosting service selected by your team. However, it remains simple and effortless as long as you have the appropriate permissions to create repositories.
Create Remote Git Repository in TFS
- Open the web portal for your TFS team project in a browser.
- Navigate to the
CODEsection using the navbar. - Open the list of repositories by clicking the small down arrow ↓ beside your TFVC repository.
-
Click
+ New repository....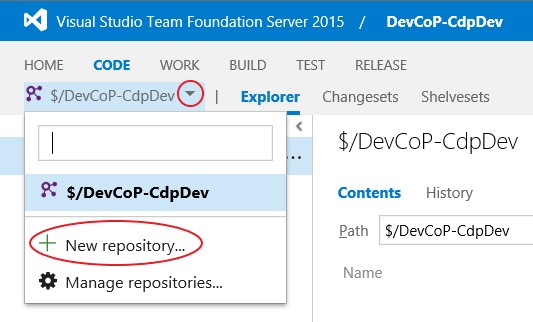
- By default, Git should already be selected as the
Type. If not, pickGitfrom the list. -
Enter the name of your new Git repository. (i.e.
my-git-repo)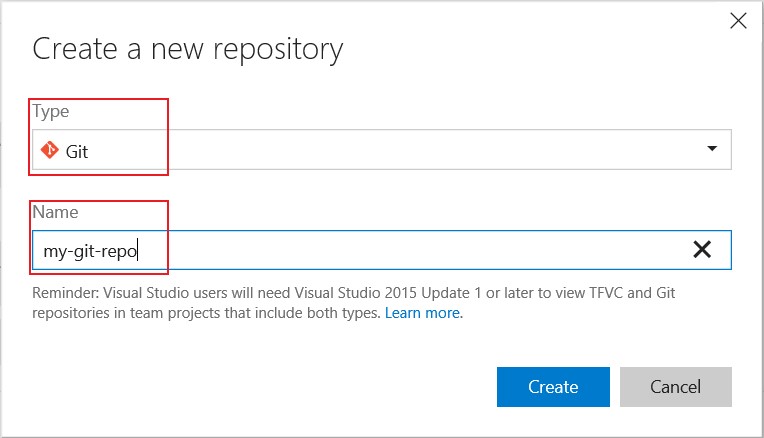
- Finally, click
Create.
Create Project in GCcode
- Open GCcode in a browser.
-
On the right side of the navbar, click the
+ (New)menu and selectNew project.
- Enter the name of your new project (i.e.
Git Playground). This will automatically fill out theProject slug. The project slugs are URL-friendly versions of project names. - Pick your team’s GCcode project for the
Project URLfield. -
Select the appropriate level of visibility for the project.
IMPORTANT : Keep in mind that GCcode is only accessible on the Government of Canada network. Therefore,
Publicmeans available to other departments and agencies. For more information about visibility, see “Subgroups - internal organizations”. - Finally, click
Create project.
Create Project in GitHub
Steps will be added shortly.
Clone TFVC to Local Git Repository
- Open a
PowerShellterminal. -
Create a folder for your local repositories (i.e.
C:\sources) and navigate into that folder.mkdir c:\sources cd c:\sources -
Download the latest Visual Studio
.gitignoretemplate from GitHub into this folder. A.gitignorefile specifies intentionally untracked files that Git should ignore. To read more about.gitignorefiles, see Ignoring Files of the Pro Git book.Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://raw.githubusercontent.com/github/gitignore/master/VisualStudio.gitignore -UseBasicParsing -OutFile .gitignore -
Add patterns to match files, folders or branches from your TFVC repository in TFS that should be ignored during this migration process. Good candidates for this include any installers, archived release branches, etc. To read more about the patterns to match items, see Git ignore patterns from Atlassian.
dev-tools-installers/ releases/ -
Create a folder to clone your Git repository into (i.e.
C:\sources\my-git-repo) and navigate into that folder.mkdir c:\sources\my-git-repo cd c:\sources\my-git-repo -
Clone your TFVC repository from TFS to a local Git repository. Don’t forget to specify the
.gitignorefile that you copied earlier!git tfs quick-clone "https://ado.intra.dmz/ProjectCollection/" "$/DevCoP-CdpDev" . --gitignore="c:\sources\.gitignore"IMPORTANT : There is a bug with the latest version of the
libgit2/libgit2sharplibrary being used bygit-tfswhich reports an unhandledSystem.AccessViolationExceptionexception. However, this is thrown during the clean-up phase after the migration which doesn’t affect the clone process. You can read more about this on the issue page for this bug. -
Add a
.gitignorefile at the root for your solution.Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://raw.githubusercontent.com/github/gitignore/master/VisualStudio.gitignore -UseBasicParsing -OutFile .gitignore - Remove secrets or encrypt as necessary.
Connect to Remote Git Repository
In order to push your local repository to your selected Git hosting service, it
needs to know where the remote repository is located. This is done by adding
a remote in with a Git command. To read more about remotes, see Working with Remotes from the Pro Git book.
The following steps will help you find the URL to your remote Git repository.
Copy remote repository URL in TFS
- Open the web portal for your TFS team project in a browser.
- Navigate to the
CODEsection using the navbar. - Open the list of repositories by clicking the small down arrow ↓ beside your TFVC repository.
-
Navigate to your project’s page by clicking on its name.
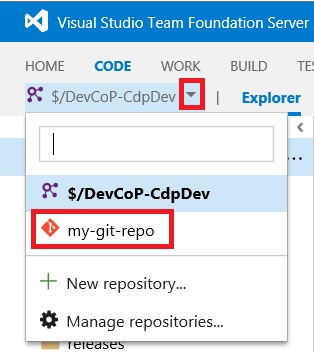
-
Click the
Copy to clipboardbutton.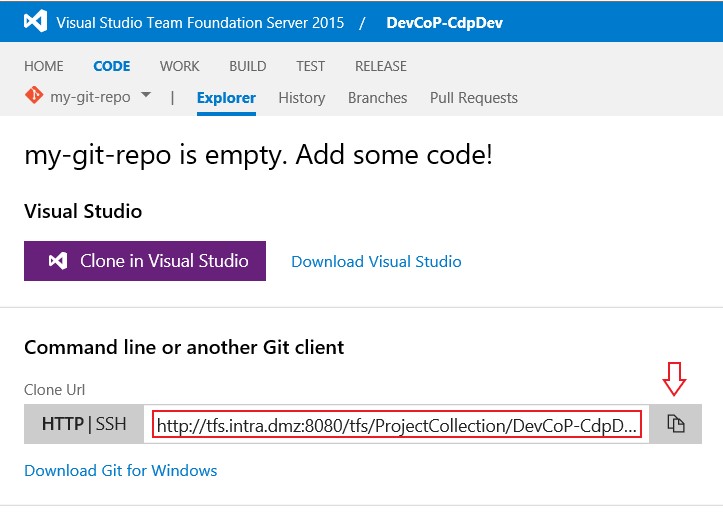
Copy remote repository URL in GCcode
- Open GCcode in a browser.
- Filter the projects to find the one your are looking for.
-
Navigate to your project’s page by clicking on its name.
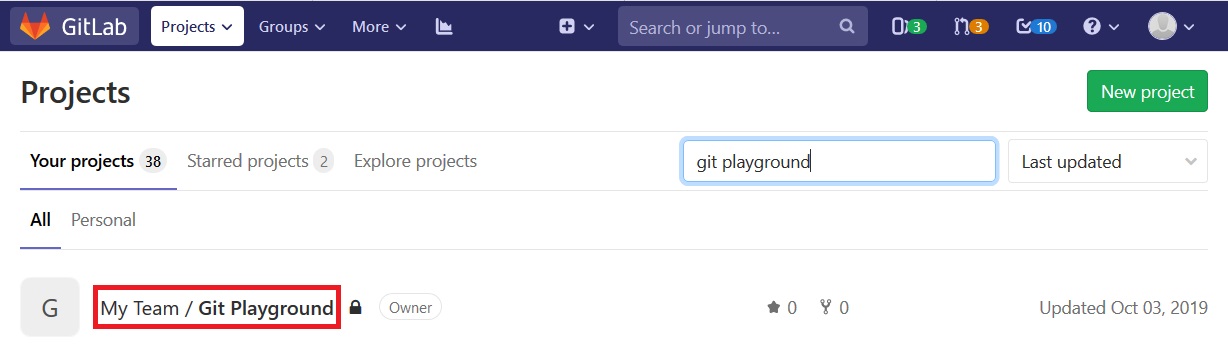
- Click the
Clonebutton on the right side of the screen. -
Click the
Copy URL to clipboardbutton.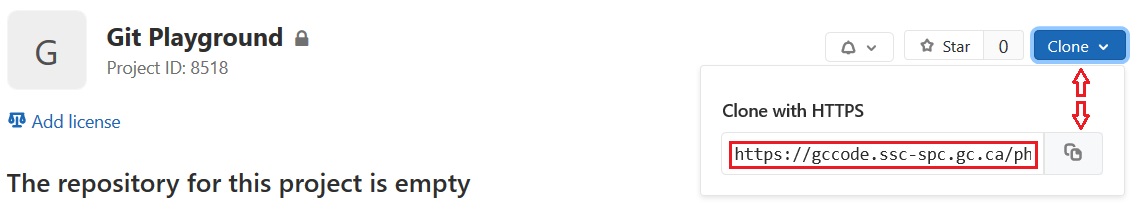
Copy remote repository URL in GitHub
Steps will be added shortly.
Connect local Git repository to remote Git repository.
-
Use the URL that you copied from the previous section to connect your local repository to the remote one.
git remote add origin "https://ado.intra.dmz/ProjectCollection/DevCoP-CdpDev/_versionControl"
Push to Remote Git Repository
-
Push local Git repository into remote Git repository.
git push --all origin -
Enter your Windows credentials as requested. If you make a typo, simply press
CTRL + Cto cancel the command and try again.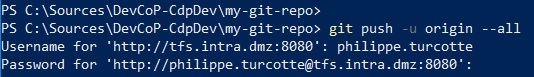
TIP : Press the up arrow ↑ to bring back the last command from the terminal’s history.
Additional Improvement
Productivity tips for your repository.
- Add Git Templates files to the Repository
- Add labels with the ESDC Label Generator (for GCcode & GitHub)
Further Reading
Learn about Git
Similar Guides
FAQ
Is it possible to migrate the code changeset history from TFSV to Git?
Did you succeeded? Should we do that?
It is possible, and we have successfully done it a few times. You can use the GitTFS tool.
There is no legal requirements for us to keep source code history, therefore we do not recommend keeping any history in the conversion. We don’t see any value in keeping it because the code is the truth of how the project functions currently (features and bugs included). If something needs to be changed, it still needs to be changed whether it was codded a specific way in the past for a reason or not. If the team still is set on keeping history, we suggest you only keep history going back one release, as the conversion will take a very long time.
Would you recommend to use the Wiki functionality for replacing our current SPECS document using MS Word?
I saw multiples interesting functionalities like the ReadMe.md (i.e.: for the file project configuration) and the Wiki section in markdown.
Personally, I see a lot of pros to use GitLab. Centralize everything, any docs at the same place.
Absolutely!!
All documentation should be, at a minimum, moved into source control. This allows you to version your documentation with the code it’s documenting. Taking it a step further to change your documentation to markdown is even better. That will allow you to track changes through your documentation, and allow you to begin to automate the documentation.
Wikis should be used to document client or user information while documentation related to development or deployments should be kept with the source code itself. You should also feel free to not use the Wiki itself at all, if all the documentation is in the source control. If you are not using a Wiki, any client or user documentation should be published to a website; GitLab Pages and GitHub Pages are both great services to host this type of documentation.
What are the real benefits of using Git into a long term perspective?
Actually, we are working with TFS and everything works fine. Why should we move to Git? What are the real benefit in short term and long term?
Even if Git is hard to start with at the begining, there is so much pro in short and long term.
The branching model
- Creating/Switch branch in Git takes miliseconds/seconds rather than minutes/hours in TFSV
- The complete repository is stored locally on your computer so you dont have any dependencies on the Network.
- It’s so easy to work with branch that you can literaly create much you want and isolate every code change or features.
- The merge tool is a way more better in Git rather than TFSV. There is less merge conflict in Git due to a strong 3 ways merge mechanism.
- Every Git platforms contains a Pull Request feature that allow every one to collaborate and share knowledge about an isolate code change or feature.
- You don’t have to check-out explicitly any changes. Everything is tracked by Git automatically.
Communuties and third party tools
- Git is the most used source version control tool in the world.
- You have a large community.
- All the new popular third party tools are designed based on Git.
- Even Microsoft made the switch. Git is now the default source control system in TFS/Azure DevOps. They also maintain the entire .NET framework on GitHub as an open source project.
- Even if you are using TFS(or Azure DevOps), GitHub, GitLab, Jira, etc. You can use Git as official source code version control system.